
Source: pixabay.com
Everyone at one time or another, has experienced a moment where they forgot what they were going to say. Perhaps it was because they got distracted, or simply because they lost their train of thought. Either way, the thought eventually returns and the conversation can carry on just as it had when it began.
This is a normal part of everyday life, but for some people, this phenomenon can be much more troublesome. Individuals with severe mental health issues can experience their version of this type of memory lapse.
Psychologists refer to the condition as "thought blocking," but unlike those momentary interruptions we all experience, individuals suffering from thought blocking are not able to recall what they were thinking.
While this is condition is not common among the general population, it can be very distressing to those affected by it. If you or a loved one is currently undergoing mental health treatment and is experiencing episodes of thought blocking, this is what you need to know.
What Is Thought Blocking?
Thought blocking is an interruption in an otherwise normal thought process that usually only affects individuals with severe mental health conditions like schizophrenia. It can occur when someone is recalling a traumatic memory but may happen anytime in a normal conversation.
At some point, seemingly for no reason whatsoever, the individual experiencing thought blocking will stop talking mid-sentence and forget what they were saying. They will remain unable to remember what they were talking about no matter how much prompting they receive or how many probing questions are asked of them.
What Causes Thought Blocking?
Thought blocking is the result of major psychiatric disorders, and is usually seen in schizophrenia. Despite most cases stemming from this condition, thought blocking has reportedly been linked to severe mood disorders and psychosis as well.
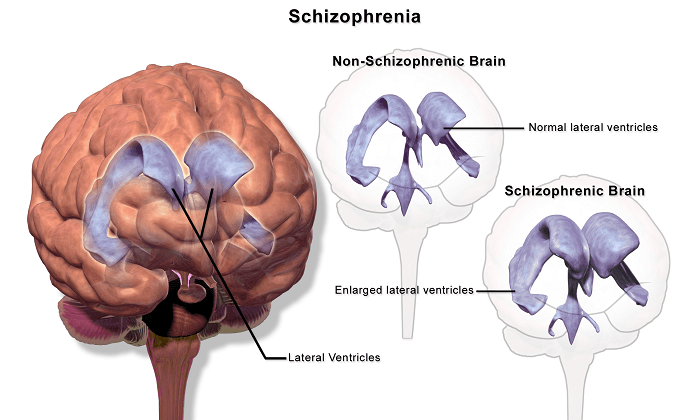
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a disorder of the brain that can cause hallucinations and delusions. Schizophrenia affects about 1% of the population and exists in both men and women. Symptoms and their effects can vary significantly between individuals, and treatment plans are specific to each patient. Schizophrenia is usually diagnosed in early adulthood and is identified through symptoms such as:
- Thought disorders
- Movement disorders
- Difficulty making decisions
- Difficulty with focus and attention
- Decreased communication skills
- Lack of emotion and expression
- Hearing voices or seeing things that are not there
- Paranoia
- Grandiose thinking
Source: commons.wikimedia.org
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a complex mood disorder characterized by intense alternating periods of high energy and depressive symptoms. Many factors contribute to bipolar disorder including genetic influences and differences in brain structure. Medical professionals can usually identify bipolar disorder through dynamic symptoms of "highs" and "lows" including:
Highs:
- Periods of increased energy and activity
- Rapid thinking
- Participation in risky behaviors (such as extreme spending, or potentially harmful sexual activity)
- Difficulty sleeping
- Anger and irritability
Lows:
- Sleeping too much
- Excess worry
- Difficulty concentrating
- Changes in eating habits
- Depressed mood
- Suicidal thoughts
Psychosis
Psychosis itself is not a medical diagnosis, but rather, a symptom of an underlying condition. Psychosis is caused by some issues including changes in sleep patterns, prescription medications, illegal drug use, injury to the brain, and mental illness. Psychosis is characterized by:

Source: pixabay.com
- Delusional thinking
- Hallucinations
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Trouble sleeping
- General loss of touch with reality
How Is Thought Blocking Diagnosed?
Thought blocking is very different from other short-term lapses in thinking. When diagnosing episodes of genuine thought blocking, mental health professionals must be certain they are eliminating other possible causes of thought interruption. Many other conditions include symptoms that mimic thought blocking including:
Severe Anxiety
Some forms of anxiety, particularly social anxiety, may be so severe that they impact an individual's ability to communicate effectively. Those who suffer from severe social anxiety may experience extreme discomfort at the thought of talking to or interacting with others. They may avoid social situations whenever possible. While thought blocking can occur in some forms of extreme anxiety, the condition itself is not caused by fear or discomfort. Episodes of thought blocking will occur despite the individuals' emotional state.
Seizures
Petit mal seizures or "absence seizures" usually occur in individuals with the condition that affects the nervous system, like epilepsy. Seizures are the result of interrupted electrical activity in the brain and typically last less than 15 seconds. When an individual experiences a petit mal seizure it can appear very similar to an episode of thought blocking. The person may stare off into the distance, stop talking mid-sentence, or stop moving altogether. After the seizure, it is not uncommon for the individual to have trouble remembering what happened. Petit mal seizures cause a person to stop all normal behavior, while the thought is blocking only impacts a person's ability to recall information.

Source: pixabay.com
Brain Injury
Some conditions, such as stroke, brain tumors, dementia, and physical trauma can cause injury or damage to the brain. If the brain has sustained major damage to areas responsible for speech and communication, it is not uncommon for an individual to struggle with talking, recalling words, or verbally communicating thoughts. Brain injury is the result of a specific condition, while thought blocking does not appear to be caused by any physical complication.
As you can see, identifying conditions where thought blocking is present, and eliminating other sources of thought interruption is a complex process. However, once the cause of thought blocking is identified, there are many things we can do to limit its effects.
How Is Thought Blocking Treated?
Because thought blocking is a symptom of an underlying issue, the underlying issue must be treated to see improvements. This usually happens in a very controlled and monitored clinical setting such as a doctor's office, therapist's office, or in-patient medical facility. Common approaches include:
Medication
Medication will vary by individual, depending on the other symptoms the psychiatric disorder presents. In the case of schizophrenia, antipsychotics are usually prescribed, but antidepressants and mood stabilizers may be tried as well.Medications will be closely monitored by a medical professional and dosages and prescriptions may change over time. If you are on medication for psychiatric disorders, it is important to take the medication exactly as prescribed. Do not miss doses. Following the doctor's orders, and communicating any changes in your thoughts, feelings, or behaviors, will be key to identifying the right medication for you.
Therapy
Many studies suggest that individuals who suffer from psychiatric conditions benefit from a treatment combination of therapy and medication. A trained therapist can teach someone to manage their symptoms, and limit the impact the symptoms have on their day-to-day life.
One method of therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, is recognized as an effective treatment method for individuals with a range of psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia. Cognitive-behavioral therapy works by helping patients understand their negative thought patterns, and encourages them to challenge the thoughts. The goal of cognitive-behavioral therapy is to use the new thought patterns to establish new, positive behaviors.
If you need help reaching out to a therapist to manage your symptoms or psychiatric disorder, let Betterhelp know today!
Support
One of the most important things for anyone experiencing any symptoms of mental illness is support. Support can come from a variety of sources including:
Family & Friends
Having a close and dependable network of people who you love and trust is key when going through treatment for mental illness. If you are caring for someone who is experiencing distressing symptoms like thought blocking, it is okay not to have answers for them.
Simply show your support by being there for your loved one, encouraging them to follow through with treatment plans, and being kind and understanding when periods of thought blocking interrupt your time together.

Source: pexels.com
Community
Sometimes, dealing with the struggles that symptoms like thought blocking can produce requires the help of others who understand the condition very well. Finding a support group made up of individuals who have a similar diagnosis or symptoms can help you, or your loved one, develop much-needed emotional support. These groups can also offer the friendship, hope, and access to coping skills that are greatly needed when managing mental illness.
Information
Learning more about thought blocking, or the underlying psychiatric condition that is causing it can provide a lot of reassurance to someone suffering from its effects. Knowledge is power, and having a strong understanding of what you or your loved one may be going through, can help you be a better advocate for their overall well-being.
Remember, doctors treat the condition based on what they learn in a book, but as the person suffering from a symptom of thought blocking, you are the expert. By staying well-informed about your symptoms and diagnosis, you can ask meaningful questions and offer valuable insight to your healthcare team. This will ensure your treatment plan is staying on track.
Thought blocking is a distressing symptom especially when someone experiences it without knowing the cause. Although it is most frequently linked to schizophrenia, thought blocking can be caused by other conditions, or even resemble something completely unrelated. If you or someone you care about is having trouble with communication or memory, it is important to speak to a doctor right away. Thought blocking could not improve unless the underlying disorder receives treatment.
Comments
Post a Comment